Infections are caused by the invasion and multiplication of harmful microorganisms, such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites, within the body. These microorganisms can enter the body through various routes, such as the respiratory tract, gastrointestinal tract, skin, or mucous membranes. Once inside the body, they can cause a wide range of infectious diseases, depending on the type of microorganism involved and the body’s immune response.
Infections can be classified based on various factors, including the type of microorganism causing the infection, the site of infection, and the severity of symptoms. Some common types of infections include:
Bacterial Infections: These are caused by bacteria and can affect various parts of the body, such as the respiratory tract (e.g., pneumonia, strep throat), urinary tract (e.g., urinary tract infection), skin (e.g., cellulitis), and bloodstream (e.g., sepsis).
Viral Infections: These are caused by viruses and can lead to illnesses such as the common cold, influenza (flu), chickenpox, measles, hepatitis, and HIV/AIDS. Viral infections can affect different organs and systems in the body, including the respiratory system, gastrointestinal system, and nervous system.
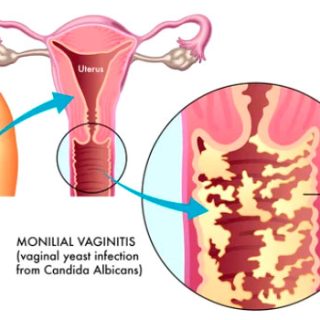
Fungal Infections: These are caused by fungi and can affect the skin (e.g., athlete’s foot, ringworm), nails, mucous membranes (e.g., oral thrush), and internal organs (e.g., fungal pneumonia). Fungal infections can range from mild and localized to severe and systemic.
Parasitic Infections: These are caused by parasites and can be transmitted through contaminated food or water, insect bites, or close contact with infected individuals. Examples include malaria, giardiasis, toxoplasmosis, and trichomoniasis.
Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs): These are infections that are transmitted through sexual contact and can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or parasites. Common STIs include chlamydia, gonorrhea, syphilis, genital herpes, human papillomavirus (HPV) infection, and HIV/AIDS.
Infections can vary in severity from mild, self-limiting illnesses to life-threatening conditions requiring urgent medical intervention. Treatment for infections typically involves antimicrobial medications, such as antibiotics, antivirals, antifungals, or antiparasitic drugs, depending on the type of microorganism causing the infection. In some cases, supportive care, including rest, hydration, and symptomatic relief, may also be necessary to help the body fight off the infection. It’s important to practice good hygiene, maintain a healthy lifestyle, and follow recommended vaccination schedules to prevent the spread of infections and protect against certain infectious diseases.